updated on Jul. 19, 2012
Manual
Getting startedDownloadYou can download the installation package here. Installation Unzip the package "yc.zip", execute "setup.exe" and follow instructions of the installer. Running Double-click the "yoshinoCALC" icon in the program of the start menu. Conventional View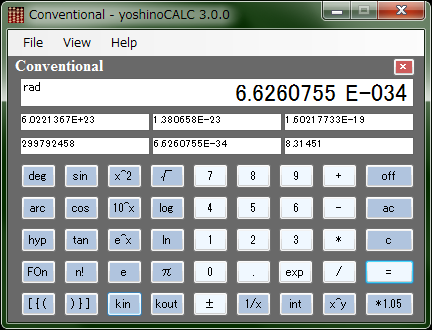 Conventional View is one of the two aspects of yoshinoCALC. The software emulates a conventional sceintific calculator. I don't think you need a detailed manual to use it. The followings are explanations for some unusual keys. deg You can change units of angle between degree and radian by pressing this key. The current unit is shown at the top-left corner of the top text box. arcThis is to calculate arcsine, arccosine and arctangent.
sin-1(0.5)*6: "." + "5" + "arc" + "sin" + "*" + "6" + "=" This is to calculate hyperbolic sine, cosine, tangent. The way of using is the same as that of arc. FOn/FOffBy clicking this button, you can turn on and off the mark "fix" at the left-bottom corner of the top text box. While "fix" is on, a small fraction less than 10-8 will be rounded. [{( and )}]These are parentheses. You can make a hyerarchy structure like below. 2*((2+3)+(5-1)): "2" + "*" + "[{(" + "[{(" + "2" + "+" + "3" + ")}]" + "[{(" + "5" + "-" + "1" + ")}]" + ")}]" kin and koutYou can store up to six results in the six smaller boxes by using the "kin" key with a number key like "kin" + "1". Press "kout"+"1" and so on to reuse a stored number. *1.05Only this key is related not to science but to economy. This key is to calculate a price of something inclding a tax. Although the tax rate is 5% in Japan now, you might want to change the rate in your country. Then right-click on the "1.05" key and select the context menu "change tax rate". A dialog window opens and you can enter a new number in a text box. The same thing can be done by selecting a menu [Help]-[Change Tax Rate]. History View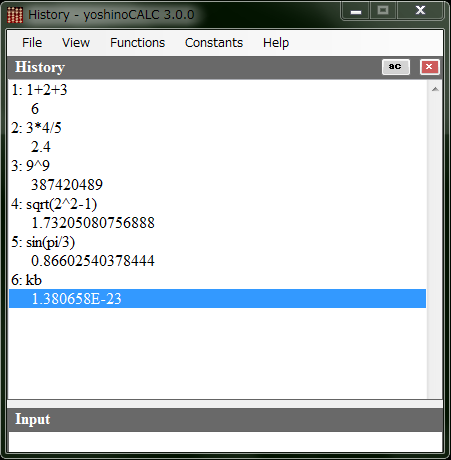 Histroy View is the other aspect of yoshinoCALC. You can evalute an expression made of following elements. The last result is copied to Clipboard as text. You can recall expressions in the list by "↑" and "↓" keys. Numbers You can enter an integer, a real number and even one with an index numbers as follows. But all the numbers will be treated as double-precision ones.
1234 You can enter π and e (Napier's number) as well as important natural constants by using following symbols. Units of the natural constants are of SI.
pi = 3.14159265358979: π (circle ratio) Basic Operations
+, -, *, /, ^
( and ) > ^ > * and / > + and -
sqrt
sqrt(.36)[enter] -> 0.6
!
5![enter] -> 120 Trigonometric Functions You can use radian as well as degree as a unit of angle in the trigonometric functions. The followings are examples of using radian.
sin
sin(pi/2)[enter] -> 1
cos
cos(-pi)[enter] -> -1
tan
tan(pi/4)[enter] -> 0.999999999999999
cosec
cosec(pi/6)[enter] -> 2
sec
sec(2*pi/3)[enter] -> -2.00000000000002
cot
cot(pi-pi/4)[enter] -> -0.99999999999999
asin
asin(1)[enter] -> 1.5707963267949
acos
acos(1)[enter] -> 0
atan
atan(1)[enter] -> 0.785398163397448
angle Hyperbolic Functions
sinh
sinh(1)[enter] -> 1.1752011936438
cosh
cosh(-1)[enter] -> 1.54308063481524
tanh
tanh(10)[enter] -> 0.999999995877693
asinh
asinh(1.1752011936438)[enter] -> 0.999999999999999
acosh
acosh(1.54308063481524)[enter] -> 0.999999999999997
atanh
atanh(0.999999995877693)[enter] -> 10.0000000224525 Exp/Log Functions
exp
exp(2)[enter] -> 7.38905609893065
ln/log
ln(el)[enter] -> 1
log10
log10(.001)[enter] -> -3 Other Functions
abs
abs(cos(pi))[enter] -> 1
sign
sign(cos(3*pi/4))[enter] -> -1
ceil/ceiling
ceil(4.2)[enter] -> 5
floor
floor(4.8)[enter] -> 4
round
round(4.2)[enter] -> 4
fix/truncate
fix(4.2)[enter] -> 4 Column View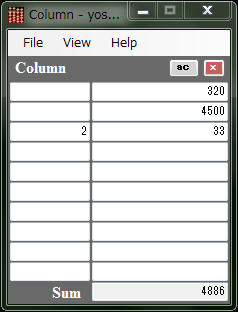 Column View is like a small spread sheet. When you need a sum of numbers, you enter them in the right column and press [Enter]. Then the sum is shown at the bottm. The left column is a multiple of each item. |
